Xenon gas is a rare, noble gas that is colorless, odorless, and denser than air. It is one of the most stable elements in the periodic table, and it has a number of interesting properties that make it useful for a variety of applications. In this article, we will explore the properties of xenon gas, its uses, and the benefits it provides.
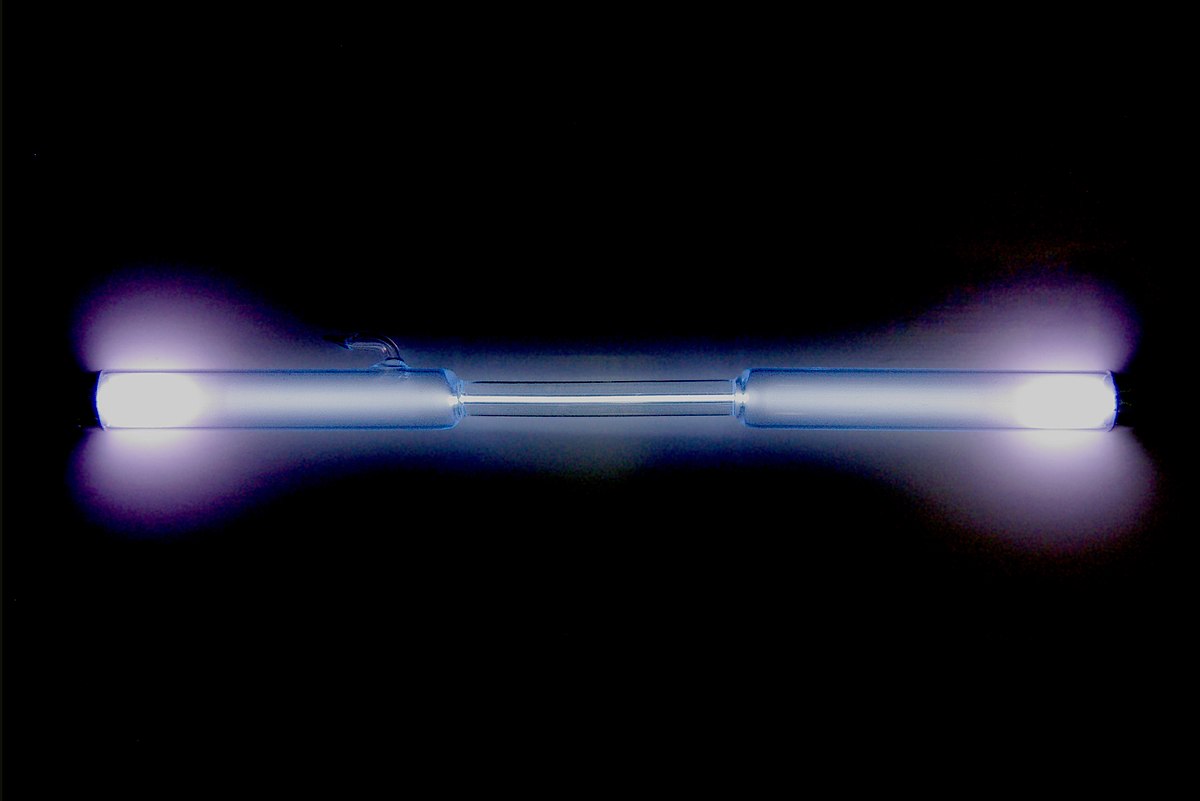
Properties of Xenon Gas
Xenon gas is a member of the noble gas family, which includes helium, neon, argon, krypton, and radon. It is the heaviest noble gas, with an atomic weight of 131.29 g/mol. Its atomic number is 54, and it is located in group 18 of the periodic table. Xenon gas has an electron configuration of [Kr]4d10 5s2 5p6, which means it has a full outer shell of valence electrons.
One of the most interesting properties of xenon gas is its high density. At standard temperature and pressure (STP), xenon gas has a density of 5.894 g/L, which is about five times denser than air. This makes it useful for applications where a high-density gas is required, such as in gas-discharge lamps and plasma displays.
Another interesting property of xenon gas is its high thermal conductivity. This means that it can transfer heat very efficiently, which makes it useful in applications such as insulation materials and cooling systems.
Uses of Xenon Gas
Xenon gas has a number of uses in industry, medicine, and scientific research. Here are some of the most common applications of xenon gas:
1. Lighting: Xenon gas is used in gas-discharge lamps, which are commonly used for automotive headlights, strobe lights, and film projectors. These lamps produce a bright, white light that is more efficient and longer-lasting than traditional incandescent bulbs.
2. Medical Imaging: Xenon gas is used as a contrast agent in medical imaging, particularly in MRI and CT scans. It is a safe, non-toxic gas that can highlight the blood flow in the body, making it easier to identify tumors, clots, and other abnormalities.
3. Scientific Research: Xenon gas is used in a variety of scientific research applications, particularly in the field of nuclear physics. It is used to detect nuclear radiation, and it can be used as a target for nuclear reactions.
4. Anesthesia: Xenon gas has been used as an anesthetic in some countries, particularly in Europe. It is a safe and effective anesthetic that has fewer side effects than some other anesthetics.
Benefits of Xenon Gas
Xenon gas offers a number of benefits over other gases, particularly in the areas of lighting and medical imaging. Here are some of the key benefits of using xenon gas:
1. Longevity: Xenon gas lamps have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs, which means they need to be replaced less often. This can save money and reduce waste.
2. Energy Efficiency: Xenon gas lamps are more energy efficient than traditional bulbs, which means they use less energy and produce less heat. This can help reduce energy costs and lower the risk of fire.
3. Safety: Xenon gas is a safe, non-toxic gas that does not pose a risk to human health or the environment. It is not flammable, and it does not react readily with other chemicals.
Conclusion
Xenon gas is a rare, noble gas that has a number of interesting properties and uses. It is a high-density gas that can transfer heat very efficiently, and it is used in a variety of applications, including lighting, medical imaging, scientific research, and anesthesia. Xenon gas also offers a number of benefits over other gases, particularly in the areas of longevity, energy efficiency, and safety. If you're interested in learning more about xenon gas and its applications, there are many resources available online and in your local library.